Community Colleges: Multiple Missions, Diverse Student Bodies, and a Range of Policy Solutions
David Baime, Sandy Baum
August 18, 2016 - Urban Institute
Abstract
Differences among community colleges present challenges for national policies that promote student access and success. Tuition is a significant barrier in some places but is covered for disadvantaged students elsewhere. Traditional success metrics carry different meanings depending on an institutionfs mission, student body, and other factors. Preparing students to transfer to four-year colleges is a central mission for some community colleges, but others almost exclusively prepare students to go directly into the workforce. Given these realities, different programmatic, pedagogical, and financing strategies will be necessary to help students meet wide-ranging goals.
Full Publication
The national commitment to increasing postsecondary educational attainment, combined with growing economic anxiety, has made community colleges the focus of many federal and state policy initiatives. There is good reason for this: by virtue of their nature and reach, community colleges—public institutions of higher education that predominantly award associate degrees and sometimes bachelorfs degrees—are indispensable to meeting national goals for educational attainment as well as for the development of a productive workforce. But no national system of community colleges exists, and national policies to improve opportunity and success at community colleges should reflect their diversity of students, programs, missions, and funding structures.
In this report, we focus on key variables that differentiate community colleges, and we elaborate on their significance for students. We first describe the range of missions and programs across institutions in this sector and explore differences in their student bodies. We then focus on student financing and national policies designed to address both affordability and broader concerns about student success. Finally, we discuss how some community colleges, frequently in partnership with states and other stakeholders, are effectively working on a student success agenda.
As with the variation across sectors of higher education, differences among community colleges present challenges for national policies designed to promote student success. Tuition is a significant barrier in some places but is covered for disadvantaged students elsewhere. Traditional success metrics carry different meanings depending on the institutionfs mission, student body, and other factors. The inadequate official federal completion rate has a larger impact on some community colleges than on others. Given these realities, different programmatic, pedagogical, and financing strategies are necessary to help students meet their wide range of goals.
The Diversity of Community Colleges
Missions and Program Mix
Unifying community colleges is their common goal of providing broad access to postsecondary education. Virtually all have open admission policies that allow students to enroll regardless of their academic preparation and achievement, although not every student has access to all programs and courses.
Most community colleges offer a wide range of programs and credentials. They aim to prepare students for either transfer to four-year institutions or immediate labor market opportunities. Other community needs and priorities also drive the creation of some programs. Some colleges devote considerable resources to offering programs that appeal to community members who view education as an end in itself rather than a means to an end. Many of these programs fall into the broad category of noncredit programs. Consistent national data are not collected on these programs, and they are something of a black box despite their wide reach.
Although most community colleges offer both occupational and pretransfer programs as well as both credit and noncredit courses, the balance varies considerably. A few examples will help illustrate.
At Glendale Community College in California, where business, management, and marketing are the most popular fields, only 8 percent of degrees are awarded in humanities, general studies, and the liberal arts and sciences. But at the Community College of Vermont, that share is 35 percent, and at Floridafs Miami Dade College, it is 61 percent. At Harry S. Truman College, part of the City Colleges of Chicago, one-third of degrees awarded are in the health professions, but at Blue Ridge Community College in North Carolina, only 12 percent of degrees are in these fields. In other words, some community colleges primarily award degrees intended as stepping stones to bachelorfs degrees, while others most often award credentials that prepare students for immediate entry into the labor force. These occupational credentials are generally terminal degrees, although options for transferring technical training credentials to four-year programs are increasing. In addition, as mentioned, community colleges have created a panoply of noncredit programs that are frequently designed to meet specific local workforce needs. Some of these programs may not lead to any postsecondary credential, but the specific skills they teach may qualify students for increasingly common employer and industry certifications.
These differences in community collegesf missions and programs complicate the measurement of student success. Under the current Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System definition of graduation rates, both students who transfer to four-year institutions without earning credentials and students who enroll for a few courses without intending to earn a degree count as noncompleters. One study found that in California community colleges, the proportion of students enrolling, successfully taking a few courses, and then leaving ranged from 8 to 84 percent (Bahr and Booth 2012). Recently, the state has probed its data on these gskill buildersh—many of whom already hold postsecondary credentials—and found that their completing courses led to significant wage gains.1 Yet federal data fail to reflect the success of these gdrop-inh students, and such students present vexing problems for measuring institutional and student success.
Community collegesf multiple missions can unintentionally undermine student success precisely because students face so many program options. Students who enroll with only the vague goal of getting a good job or getting more education may, without proper academic counseling, wander through a variety of courses, accumulating neither the building blocks of a specific career nor the courses necessary for transfer to a four-year institution. The gshapeless riverh of many community colleges (Scott-Clayton 2015), with their multitude of offerings, can easily end up derailing students. (We address this problem below in our discussion of structured pathways.)
Demographics
As locally oriented institutions, the demographics of community colleges reflect their surrounding areas. Community colleges enroll higher percentages of female, first-generation (36 percent), low-income, and minority students than any other sector of nonprofit higher education. Community colleges enroll 52 percent of all African American and 57 percent of all Hispanic students in higher education (AACC 2014), but the demographics vary considerably across institutions.
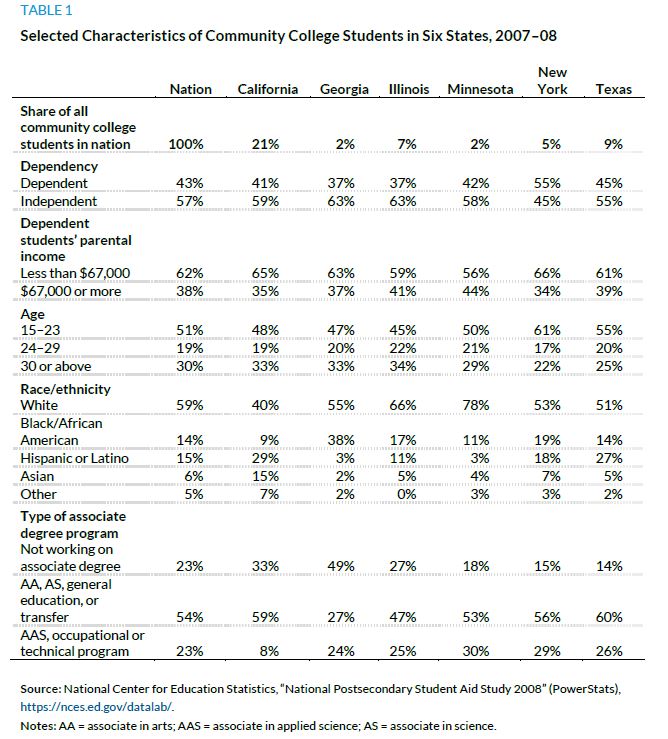
In 2007–08, the Department of Education collected data on California, Georgia, Illinois, Minnesota, New York, and Texas to provide insights into demographic variation across community colleges (table 1). Two-thirds of community college students in Georgia and Illinois, but less than half of those in New York, were independent—that is, age 24 or older, married, with children of their own, or meeting other specific criteria making their parents irrelevant to their financial aid eligibility. Age differences corresponded to dependency status across states: 61 percent of students in New York community colleges were age 23 or younger compared with just 45 percent in Illinois.
In the nation as a whole, 59 percent of 2007–08 community college students were white, but in the six states for which data were gathered, the range was from 40 percent in California to 78 percent in Minnesota. In Georgia, 38 percent of students in the sector were black compared with 9 percent in California, where 29 percent were Hispanic, which is about twice the national average of 15 percent.
The Department of Education data also confirm the differences in community college programs. The proportion of students pursuing general education or transfer degrees ranged from 27 percent in Georgia to 60 percent in Texas. Thirty percent of Minnesota students were pursuing occupational or technical associate degrees compared with 8 percent of those in California.
More recent data on racial/ethnic characteristics confirm that community colleges have seen rapid growth in their Hispanic student populations. In 2013, half of all community college students across the nation were white, down from 59 percent in 2007-08. The percentage of students who were Hispanic had increased to 21 percent, and 15 percent were black (table 2). But 21 percent of all students in the sector were in California, where 41 percent were Hispanic and only 29 percent were white. Another 9 percent of the nationfs community college students were in Texas, where 38 percent were Hispanic. Only 13 percent of the sectorsf students outside these two states were Hispanic. Excluding these two states lowers the percentage of Hispanic students in community colleges from 21 to 13 percent and increases the percentage of white students from 50 to 58 percent.
Community College Financing
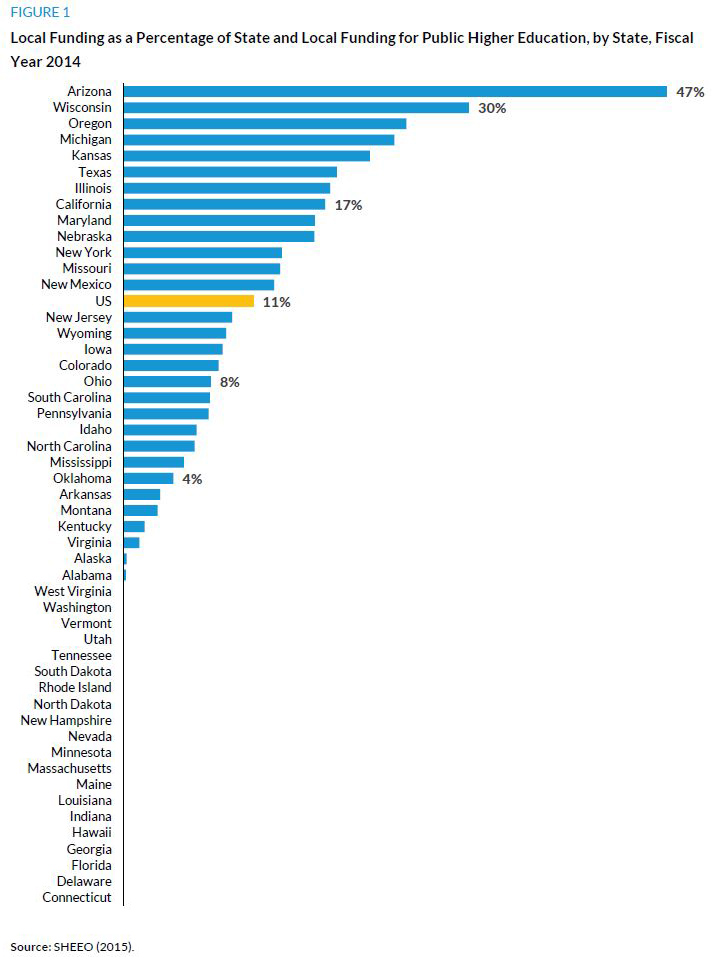
Most public higher education institutions, including community colleges, are financed through a combination of state appropriations and tuition revenues. In addition, local funding is a key element for community colleges in about half the states (SHEEO 2015; figure 1). Almost half of Arizonafs community college funding has come from local governments since the state has withdrawn support for three of its major community colleges.
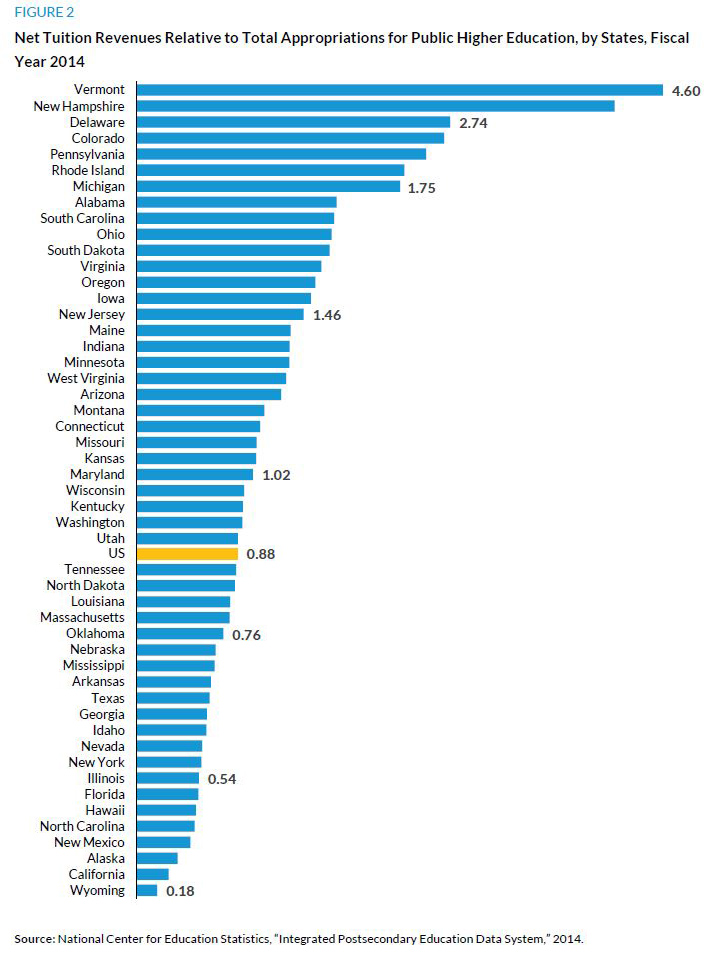
Virtually all community colleges have become increasingly reliant on tuition as a revenue source. In the 10 years ending in 2012–13, the percentage of education and related expenditures covered by net tuition revenue rose from 26 to 39 percent, reflecting the broader state government disinvestment in higher education (Ma et al. 2015).
In the nation as a whole, the revenue public colleges and universities receive from tuition payments is 88 percent as high as state and local appropriations. In other words, tuition and fee payments from students and families (with assistance from federal and state grant aid) constitute almost half of the revenues (figure 2). But subsidies from public funding play a larger than average role in many states, including Wyoming, California, Alaska, and New Mexico, where tuition revenues are less than half as large as appropriations. In contrast, some states depend much more heavily on tuition revenues. In Vermont and New Hampshire, tuition revenues are more than four times as high as appropriations, and in another five states they are more than twice as high.2
Prices
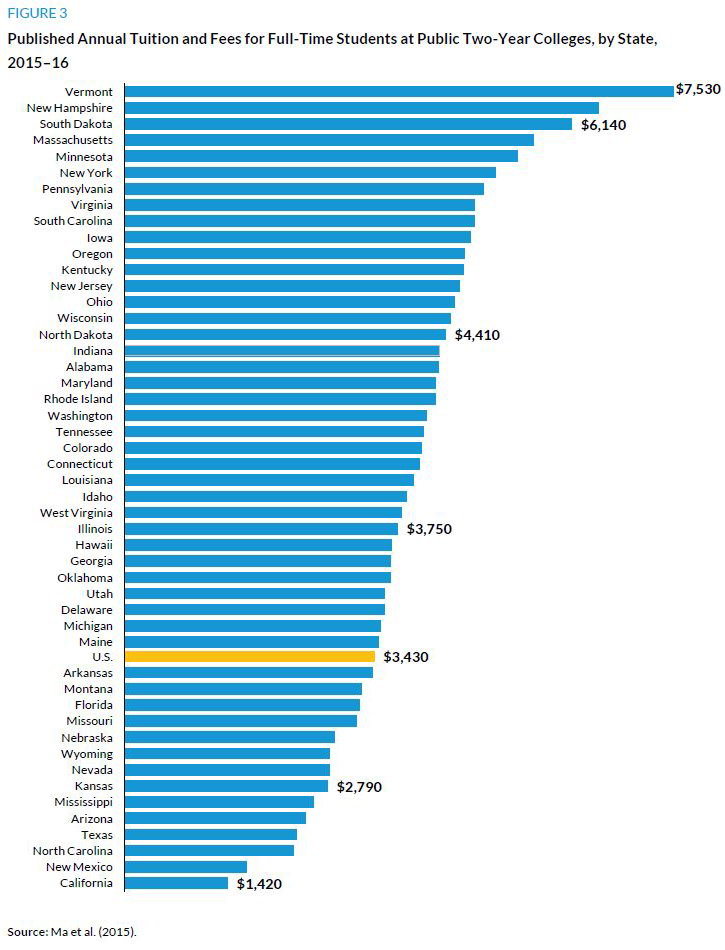
Not surprisingly, these different financing structures create large differences in community college tuitions. Community college students in similar financial circumstances will encounter dramatically different financial barriers to attendance depending on where they live. In 2015–16, the average published annual tuition and fee price for full-time students at community colleges was $3,430 (figure 3). But in California, where 21 percent of the nationfs community college students are enrolled (Snyder, de Brey, and Dillow 2016), community colleges charged full-time students $1,420, and a generous tuition waiver program benefits students with incomes below 150 percent of the federal poverty level for their family size. This tuition waiver applies to more than 50 percent of all students and represents over $800 million in assistance; it is outside of any federal or state grant aid students receive. However, living costs in California are higher than in most parts of the nation, placing a different but no less challenging financing burden on students.
At the other end of the tuition spectrum, the Community College of Vermont had a published annual price of $7,530 for 2015–16. In that state, only 21 percent of public college students are enrolled in the two-year sector compared with about 60 percent in California, Illinois, and Wyoming. These discrepancies have enormous policy implications for state financial aid programs and other efforts to increase educational opportunities.
As discussed, Californiafs community colleges vary substantially by mission. About 10 percent of the statefs 113 community colleges are small, enrolling fewer than 1,000 full-time equivalent students. Another 10 percent have more than 7,000 students. But all of them charge the same low price. In contrast, published annual tuition and fees range from about $1,600 to over $4,000 at Texas community colleges and from $2,600 to $4,800 in Michigan, where the student bodies range from fewer than 500 students to more than 8,000.
Given this reality, making community college tuition free—or setting any other fixed level of tuition and fees across the nation—would have different effects on each state budget and student body. State and local gPromiseh programs are designed to convey the simple message of universal free community college and sometimes of free tuition at other public institutions. Evidence suggests that this approach can elicit greater higher education participation. Many state and local Promise programs share some basic features, but they have important differences as well. Perhaps the most significant is whether the program is glast dollarh or gfirst dollar.h A first-dollar program simply eliminates tuition charges, as in President Barack Obamafs proposed Americafs College Promise plan and federal legislation modeled on it. Low-income students could then use federal grant aid to help with books, supplies, transportation, and living expenses. Last-dollar programs, such as Tennessee Promise, instead fill in the gap between existing grant aid and tuition and fees. With this approach, only students who do not qualify for need-based grants to cover community college tuition receive incremental funds. The distributional implications of these approaches are starkly different. Moreover, differences in the additional subsidies each plan delivers vary dramatically depending on current tuition and fees.
State Grants
Eligibility for federal Pell grants is the same regardless of state of residency. But different state grant policies can lead to very different net prices for students facing similar published tuition and fees.
In 2013, the share of all first-time full-time community college students receiving any form of grant aid ranged from 48 percent in New Hampshire to 94 percent in South Carolina (Ma and Baum 2015). Nationwide, 28 percent of students in all sectors of higher education received state grant aid. By state, this ranged from 64 percent in South Carolina and 59 percent in Oklahoma to 2 percent in Utah and zero in New Hampshire (NASSGAP 2014).
Community college students in Idaho, Maine, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Mexico, and Washington, DC, were not eligible for state grant aid in 2013–14. In another 12 states, grant aid per community college student averaged less than $100. But the average was over $1,000 per student in Florida and Georgia and above $500 in four additional states.3
California, New Mexico, and North Carolina have the lowest community college tuition rates. California and New Mexico provide little state grant aid to community college students (outside of the generous California fee waiver mentioned), but North Carolina awarded about $220 per student in 2013–14. South Dakota, New Hampshire, and Vermont have the highest community college tuition rates. South Dakota and New Hampshire provide virtually no state grant aid to community college students, but Vermont awarded about $260 per student in 2013–14.4
These differences in state grant policies can either reinforce or partially compensate for tuition differences. The net prices students pay for community college tuition vary quite a bit across the nation. Estimated 2015–16 tuition and fees net of all grant aid ranged from a low of -$2,290 in New Mexico to more than $4,000 in New Hampshire and Vermont (Ma and Baum 2015). Average estimated grant aid exceeded the published tuition and fee prices at community colleges in 19 states, leading to negative net prices when living costs were not considered.
When we add housing and food costs (but not books, transportation, and other living expenses), the average estimated annual net price of community college tuition in 2015–16 ranged from under $5,000 in Delaware and Mississippi to over $13,000 in Hawaii, Vermont, and New Hampshire (Ma and Baum 2015).
In other words, even before looking at income levels and cost-of-living differences, tuition tells only part of the story of state-to-state differences in community college affordability.
Community collegesf relatively low net tuitions do not eliminate financial challenges for students. First, the tuition price does not include the reality of living expenses. Many community college students struggle to earn a family-sustaining wage. In 2011–12, 43 percent of all community college students and 24 percent of those enrolled full time worked full time while they were in school.5 But working full time makes succeeding in college even more difficult than it would otherwise be, and this is magnified for students who suffer from inadequate academic preparation.
Student Financing
Differences in tuition prices and state grant aid, wide variation in incomes and cost of living across the country, and a range of personal circumstances facing students at different stages of life make it difficult to generalize about the pressures of financing a community college education. For some students, paying tuition and buying books and supplies is a real challenge. Yet for many others, these expenses are limited and the real issue is covering living expenses, often without labor market earnings. But financial strains are far from the only factor interfering with community college success. Poor academic preparation, institutional structural and resource constraints, personal and family responsibilities, and conflicting priorities all contribute to disappointing completion rates. Clearly, no one simple solution to these problems exists.
Access to Funds
Even students who do not have to pay tuition need to cover their living expenses. Although many community college students work, earning enough to support themselves, and frequently their families, can be an uphill battle. This makes accessing available financial aid of critical importance. Sometimes even small amounts of funding can make the difference in continuing enrollment.
Unfortunately, however, many community college students do not even apply for federal student aid. In 2011–12, 37 percent of community college students did not complete a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Independent students with dependents were least likely to apply. Among dependent students, application rates declined as family income levels increased, but 15 percent of students from the lowest family income quartile and 29 percent from the second quartile, most of whom would likely be eligible for federal grant aid, did not apply. Students enrolled less than half time were least likely to apply for federal aid, but 24 percent of full-time community college students did not complete the application process.
Despite the complexity of the FAFSA being emphasized as a barrier to completion, evidence suggests that a greater cause is simply that enrollees do not foresee the expenses involved in attending community college (particularly nontuition expenses) and do not know that student aid is available to them. When 2011–12 community college students were asked why they did not complete the FAFSA, 44 percent of non–aid applicants said they thought they were ineligible. The second most common response was that they thought they had no need. Others were reluctant to take on debt. Only 15 percent said they had no information about how to apply, and 9 percent said that the forms were too much work.6 Reluctance to become entangled with a federal agency, particularly among new residents, may also be a cause.
These different reasons for not applying for aid make increasing the number of students applying for federal aid challenging. But the government, private agencies, and community colleges have launched several efforts to provide guidance and assistance in completing the FASFA. For example,
- Montgomery County Community College in Pennsylvania offers periodic FAFSA completion workshops at high schools;
- Clackamas Community College in Oregon has a new FAFSA lab where parents, students, and other community members can come for assistance;
- Broward College in Florida has a partnership with the K–12 public school district superintendent, high school principals, guidance counselors, and community organizations to host FAFSA completion workshops; and
- Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College in Mississippi partners with the Get to College Now organization to assist high school students and parents with completing the FAFSA.
Student Loans
Community college students are less dependent on loan financing than those in other sectors. In 2011–12, 39 percent of all first- and second-year undergraduates borrowed. Across sectors, these percentages ranged from 21 percent in community colleges to 76 percent in for-profit institutions. Eleven percent of community college students borrowed more than $3,000 that year compared with 27 percent of first- and second-year students overall.
Nonetheless, significant controversy exists about the extent to which community college students should borrow and about the role institutions should play in counseling students about taking on debt. Some community college officials argue that if grant aid covers tuition and some other charges, students should have no need to borrow. In fact, almost 10 percent of community college students are enrolled in institutions that do not participate in the federal student loan program (Institute for College Access and Success 2014). One motivation for this decision is concern that high default rates might jeopardize the collegesf eligibility for all federal aid programs, including Pell grants. This aid policy is another factor creating sharp differences in the circumstances community college students face and the opportunities they enjoy.
But as many advocates for students argue, working too many hours to cover living expenses can diminish student success. Working more and taking fewer courses to avoid borrowing may be shortsighted compared to relying on loans to supplement other resources, graduating as quickly as possible, and using part of the earnings premium from the degree completed to repay the loans.
Information about aid can make a difference in student decisions. The Connecticut Community College system automatically informs students about how much aid they would qualify for as full-time students even if that is not their current enrollment preference or status. This simple step can drive greater enrollment intensity because it shows students that that enrolling full time is financially feasible (Klempin 2014).
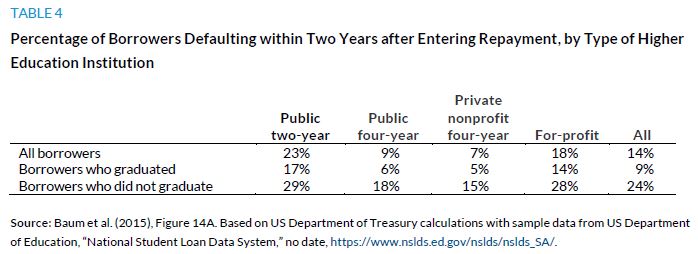
The issue of community college debt is greatly complicated by evidence on the default rates of those who do borrow (table 4). Like borrowers in the for-profit sector, those who complete community college credentials are about as likely to default as noncompleters in public and private nonprofit four-year institutions (Looney and Yannelis 2015). But these data are easy to misinterpret because the percentage of students borrowing is so much smaller in community colleges than in for-profit institutions. Just as significantly, community college students borrow far less than for-profit sector students. However, it is students with smaller loan balances who are most likely to default; defaults are concentrated among students who do not complete their studies and therefore do not have the opportunity to amass larger amounts of debt.
Strategies other than barring access to federal student loan programs might facilitate student success while guarding against overborrowing. For example, part-time students are currently subject to the same annual loan limits as full-time students. Making this policy consistent with the prorating of Pell grants in accord with enrollment intensity would prevent part-time students from taking on excessive debts. It might also be possible to grant institutions the authority to reduce loan amounts for individual students or programs. The policy would have to be designed to avoid discriminatory practices, but students who lack adequate academic preparation, come to community college with large debts, or are enrolled in programs whose graduates tend to have low earnings might be given lower borrowing limits than others.
Access to Other Funds and Resources
Notwithstanding the substantial federal investment in student aid, many community college students need additional financial support to meet their expenses. Because of the time students must devote to their schooling, many, particularly those with family responsibilities, do not have the earnings they could have if they were not in college. Access to other public funds can help mitigate this problem. Several community colleges have implemented Single Stop programs, which provide information about and coordinate access to state nutrition assistance, child care assistance, and other state and federal support programs. The president of Macomb Community College, an innovator in this area, considers this sort of program one of the most important retention strategies available to community colleges.7
Other Barriers to Student Success
Financial strain is not the only factor, nor in many cases the most significant factor, interfering with community college students meeting their goals. Analysts and policymakers are directing considerable attention to the problems of inadequate academic preparation, ineffective developmental education, and the need for more structured pathways through community colleges. Some community colleges are aggressively pursuing reforms that can significantly increase their studentsf success rates. Others lack the resources, knowledge, or motivation to take these steps. These differences could create even greater variation in community collegesf effectiveness.
Salient examples include the implementation of structured pathway programs to guide students toward their goals, improved transfer processes, and reform of remediation.
Guided Pathways
After more than half a decade of intense national focus on improving community college graduation rates, there has been little if any progress (Shapiro et al. 2015). Stagnation, at best, in completion rates is not for want of trying: the goal of improved completion has become the North Star at the vast majority of community colleges. A gcompletion commitmenth signed by the American Association of Community Colleges and five other community college organizations in April 2010 aimed to increase completion rates by 50 percent over the decade. Much attention is now turning to the guided pathways reform movement as an evidence-based strategy for tackling this seemingly intractable problem.
Thomas Bailey and coauthors described the concept of guided pathways in detail and forcefully articulated its justification in their recent book (Bailey, Jaggars, and Jenkins 2015). The basic idea is that community college students are much more likely to attain degrees if they follow a structured, logical progression to a defined credential rather than confronting a wide array of academic options. Without appropriate guidance, many community college students, lacking the necessary information about how to achieve their goals, make suboptimal academic choices. To be effective, programs must monitor studentsf movement along the structured path, reinforcing and supporting their progress through a variety of institutional services, including intensive counseling. Despite convincing evidence of the positive effects of guided pathways, these reforms necessarily entail significant institutional change, as well as resources. As a result, not all community colleges will likely be able to overcome the barriers of internal resistance to change and find the necessary resources.
Compelling students to make choices early on about their courses of study and providing strong direction that might limit academic exploration may raise concerns about access to a broad education. But guided pathways can be designed to allow intellectual inquiry while still prioritizing on-time graduation.
Some examples of successful reformers include Sinclair Community College, which has implemented Career Communities. In this program, entering students choose a broad program area and must choose a specific major after their first year. Career Communities students receive embedded advising upon entry and at critical points throughout their academic careers. Sinclair has mapped all of their programs with recommended general education courses and electives—a process led by their faculty. An electronic system tracks students along their academic plans and provides interventions when students deviate from those plans. The City Colleges of Chicago have also completely reorganized around career clusters that include more specific program maps once students choose a program of study. Completion rates have more than doubled since this systemic reform was implemented, consistent with the guided pathways approach (Kazis 2016). Queensborough Community College also provides detailed program maps for students to expeditiously complete degree programs.
There are surely other paths to increasing completion rates. A simple emphasis on better academic advising could yield strong results. But community colleges that successfully implement systemic reforms guided by the structured pathways movement will likely differentiate themselves from those that leave students to navigate a gshapeless riverh (Scott-Clayton 2015).
Transfer
In addition to providing the education and training students need to enter specific occupations, community colleges prepare many students to transfer to four-year institutions and earn bachelorfs degrees. The percentage of students earning bachelorfs degrees who spent any time in community colleges varies dramatically across the country, ranging from just 16 percent in Alaska and 24 percent in Massachusetts and Rhode Island to 66 percent in Kansas and Wyoming and 70 percent in Texas (National Student Clearinghouse Research Center 2015).
The tensions among the multiple functions of community colleges are significant, particularly because the labor market value of attaining baccalaureate relative to sub-baccalaureate credentials continues to grow,8 increasing the importance of transfer. Yet general associate degrees designed to parallel the first two years of bachelorfs degree study have much lower returns in the labor market than more technical, occupation-specific associate degrees (Backes, Holzer, and Velez 2014; Jacobson and Mokher 2014). In other words, there is no easy answer to how individual community colleges should balance these pathways.
What is clear, however, is that state- and institution-based articulation programs and other strategies for carefully guiding students through the transfer process could increase the number of community college students who go on to earn bachelorfs degrees. Not surprisingly, the loss of credits in transfer is correlated with reduced academic success at the subsequent institution (Mullin 2012). Losing credits also increases time to degree and the costs students incur. Sixteen states have statewide common course numbering, and 31 states have statewide guaranteed transfer of an associate degree, but the others do not.9
State policies make a difference, as do different practices at institutions with similar missions and student bodies. Fourteen percent of students beginning community colleges in 2007 eventually earned bachelorfs degrees, but in nine states, less than 10 percent achieved this outcome. The lowest rates were 2 percent in South Dakota and 5 percent in West Virginia. In contrast, 18 percent of students in Wyoming, Montana, and Maryland earned bachelorfs degrees within six years of beginning community college (Jenkins and Fink 2016).
In some states, legislators or other officials have mandated that institutions adopt and implement transfer-friendly policies. These include establishing blocks of programs or entire degrees that transfer en toto to a four-year program; common course numbering across institutions; and setting routine reviews of studentsf prior academic achievements. Unfortunately, experience shows that seamless transfer requires vigorous monitoring of institutional practices, not simply formal requirements. In addition, students should be advised of any available transfer opportunities as early as possible, ideally before they have committed to specific coursework. Institution-based program-to-program articulation agreements can provide the focus lacking in statewide frameworks.
Some states, community colleges, and public higher education systems are working hard to improve transfer routes. Students enrolling in institutions not benefiting from effective transfer policies will likely face more limited options and lower success rates than those seeking bachelorfs degrees after beginning in community colleges more engaged in these efforts.
Developmental Education
Startlingly low success rates in developmental education courses, which have become academic dead ends for thousands of students (Bailey and Cho 2010), are leading to innovative reforms in many states and on many community college campuses. Virginia, Texas, Florida, Connecticut, and other states are implementing changes that include these promising elements:
- New instruments used to assess student abilities: This approach includes replacing one simple cut-off score with more nuanced measures of academic strength, which might incorporate high school grades in addition to test results.
- Restructured developmental education courses: Some institutions allow students to take modular courses to address specific weaknesses rather than semester-long developmental courses covering knowledge students may already have. For example, Austin Community Collegefs Accelerator allows students to focus on particular shortcomings and provides immediate academic support.
- Allowing students to skip developmental courses entirely: Florida no longer requires students who graduated from high school after 2007 to take a placement exam or to enroll in remedial courses.
- Enrolling students in developmental courses or providing ongoing academic support at the same time they pursue credit-bearing courses that count toward their degrees. Complete College America has championed this gcorequisiteh model, which Tennessee, Indiana, and West Virginia have adopted statewide (Complete College America 2016). An evaluation by the Community College Research Center showed that in Tennessee, corequisite remedial education has proven to be cost effective compared to the previous traditional model (Belfield, Jenkins, and Lahr 2016). The Community College of Baltimore County has received national attention for providing academic support for students who would otherwise enroll in remedial courses, but who instead are allowed to take gateway courses.
Community colleges are also actively fashioning arrangements with secondary schools to reduce—if not eliminate—the need for remediation. One promising practice is to administer placement tests to high school students; those who do not meet college standards can enroll in courses designed to bring them up to that level by the time they graduate. The needed instruction can take place through dual enrollment programs or during the summer. This approach has had a positive effect in Maryland, Tennessee, and Illinois. Variations on it are becoming increasingly widespread.
Colleges are embarking on other strategies to achieve success. Dual enrollment programs allow high schools students to earn community college credit. More intensive and sophisticated academic supports, often based in technology, are also taking hold in many places.
The potential role for the federal government in these institutional practices remains undefined. The governmentfs involvement in undergraduate education is predominantly student aid, and most stakeholders agree that this is appropriate. But as the federal investment in students grows along with the pressure for institutional outcomes to improve, calls are growing for greater engagement in a myriad of modes.
Conclusion
Community colleges play an essential role in creating postsecondary education and training opportunities for millions of Americans. Open admission policies and relatively low tuition prices open the door to many students who would otherwise not be able to continue their educations beyond high school. But ensuring that the opportunities are meaningful and lead to beneficial outcomes requires a clear understanding of community collegesf wide range of missions, students, circumstances, and outcomes across the nation.
Community college leaders and public policymakers are well aware that focusing only on enrolling students is not enough. Students face different financial barriers depending not only on their circumstances but also on the tuition prices they pay, the grant aid for which they are encouraged to apply and are eligible, the access to federal loans that facilitate their financing, and the local cost of living. Prospects for studentsf success depend on what programs are available at their local institutions, how much support and guidance they get in choosing and navigating these programs, and how well these programs are structured to lead to successful labor market outcomes or further education.
Understanding the variation across community colleges is only a first step. But it is a step that lays groundwork at the federal, state, and local levels for a more nuanced and productive discussion about strengthening community colleges and their studentsf outcomes.